Publications IMAA M&A Review: Reflections on Resetting the Bar in M&A
- Publications
IMAA M&A Review: Reflections on Resetting the Bar in M&A

SHARE:
Executive Summary
IMAA’s 2023 mergers and acquisitions review highlights a transformative period for the global M&A market, which in 2023 faced a substantial downturn, witnessing a 25% decline in deal volumes and a 31% decrease in deal values compared to the previous year. This decline was influenced by various factors, including the impact of rising interest rates, inflationary pressures, geopolitical uncertainties, and concerns regarding a potential recession.
However, amid the overall downturn, a few positive trends emerged in the M&A landscape during 2023. Firstly, there were indications of a revival in activity, particularly notable in the fourth quarter of the year. Secondly, there is a growing adoption of AI tools by dealmakers, aiming to enhance efficiency and reduce costs in the M&A process. Lastly, smaller deals are displaying increased resilience, with expectations of a quicker recovery compared to larger deals in the forthcoming quarters.
Overview
How 2023 Ended for M&A
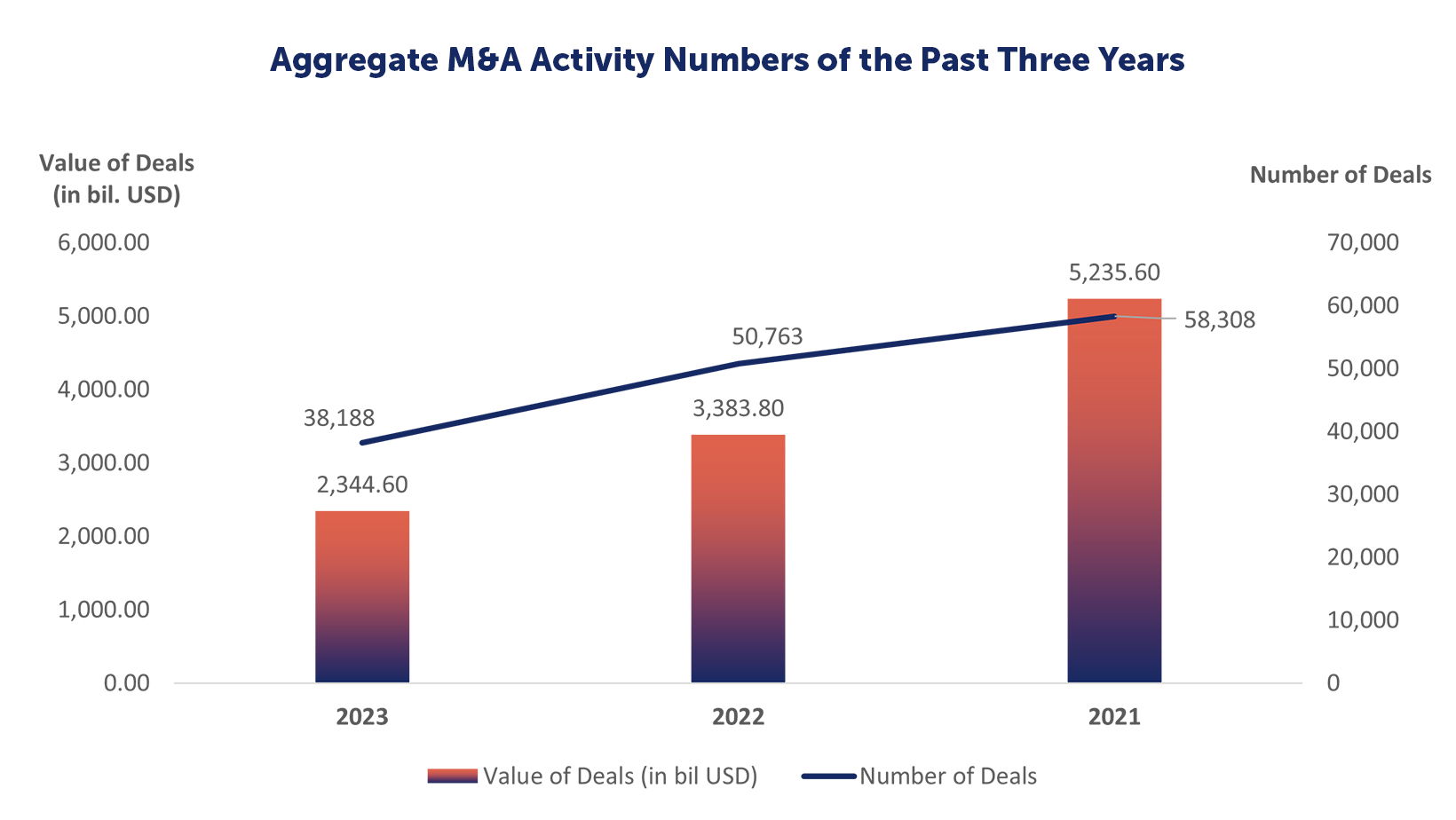
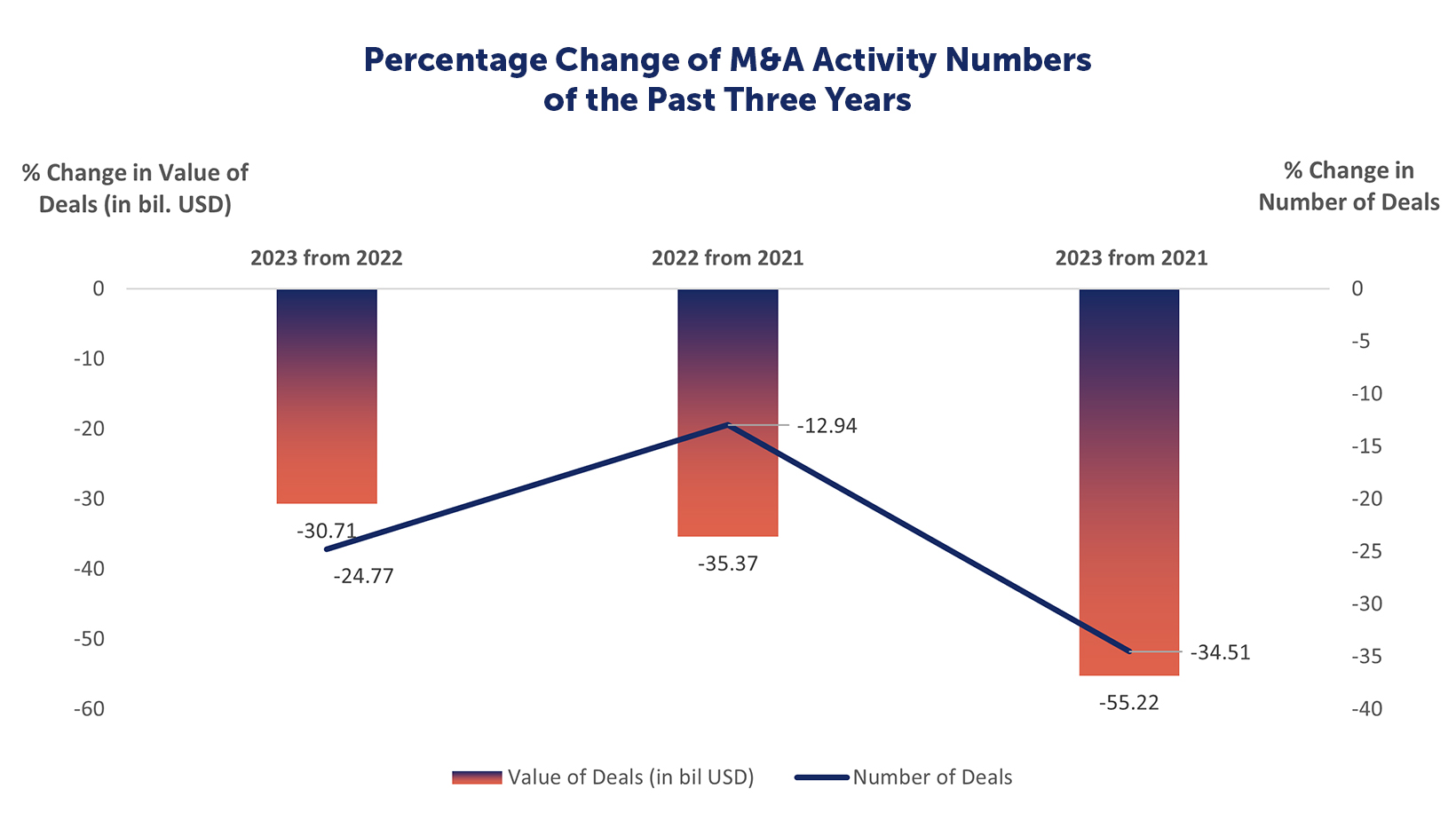
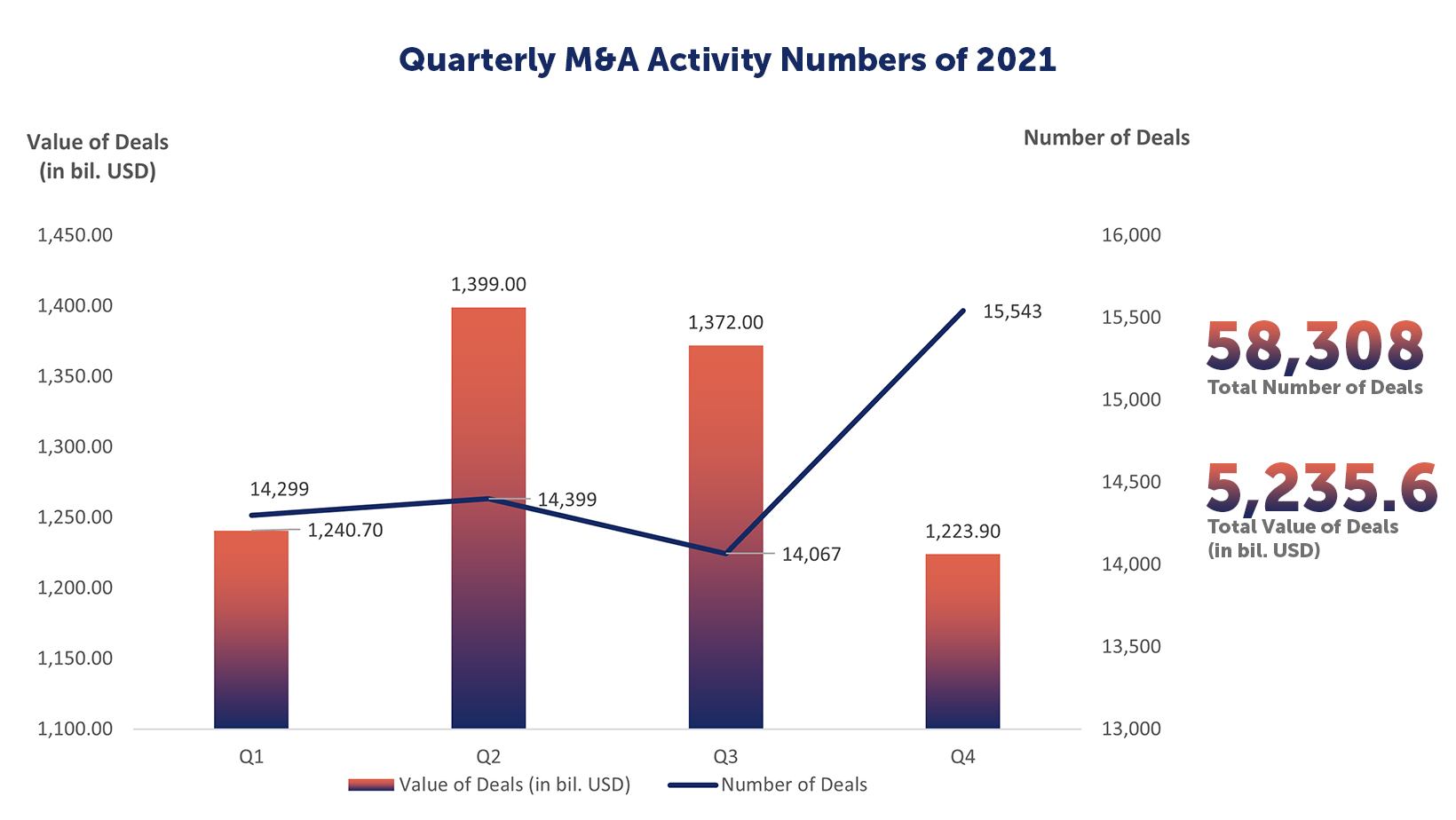
As of the writing of this report (December 14, 2023), there have been 38,188 M&A deals globally in 2023 with a value of USD 2,344.5 billion (USD 2.34 trillion). These figures compared to the previous year (2022) indicate that in 2023, M&A faced a decline of 25% in number of deals and a 31% decline in value of deals, and when compared to 2021, number of deals have declined 35% and value of those deals by 55%. The M&A deals for 2022 in comparison to 2021 had a 13% decline in number of deals and a 35% decrease in the value of those deals.
Table 1:
Aggregate M&A Activity Numbers of the Past Three Years
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 |
Number of Deals | 38,188 | 50,763 | 58,308 |
Value of Deals | 2,344.6 | 3,383.8 | 5,235.6 |
Table 2:
Percentage Change of M&A Activity Numbers of the Past Three Years
| Percentage Change 2023 from 2022 | Percentage Change 2022 from2021 | Percentage Change 2023 from 2021 |
Number of Deals | -24.77 | -12.94 | -34.51 |
Value of Deals | -30.71 | -35.37 | -55.22 |
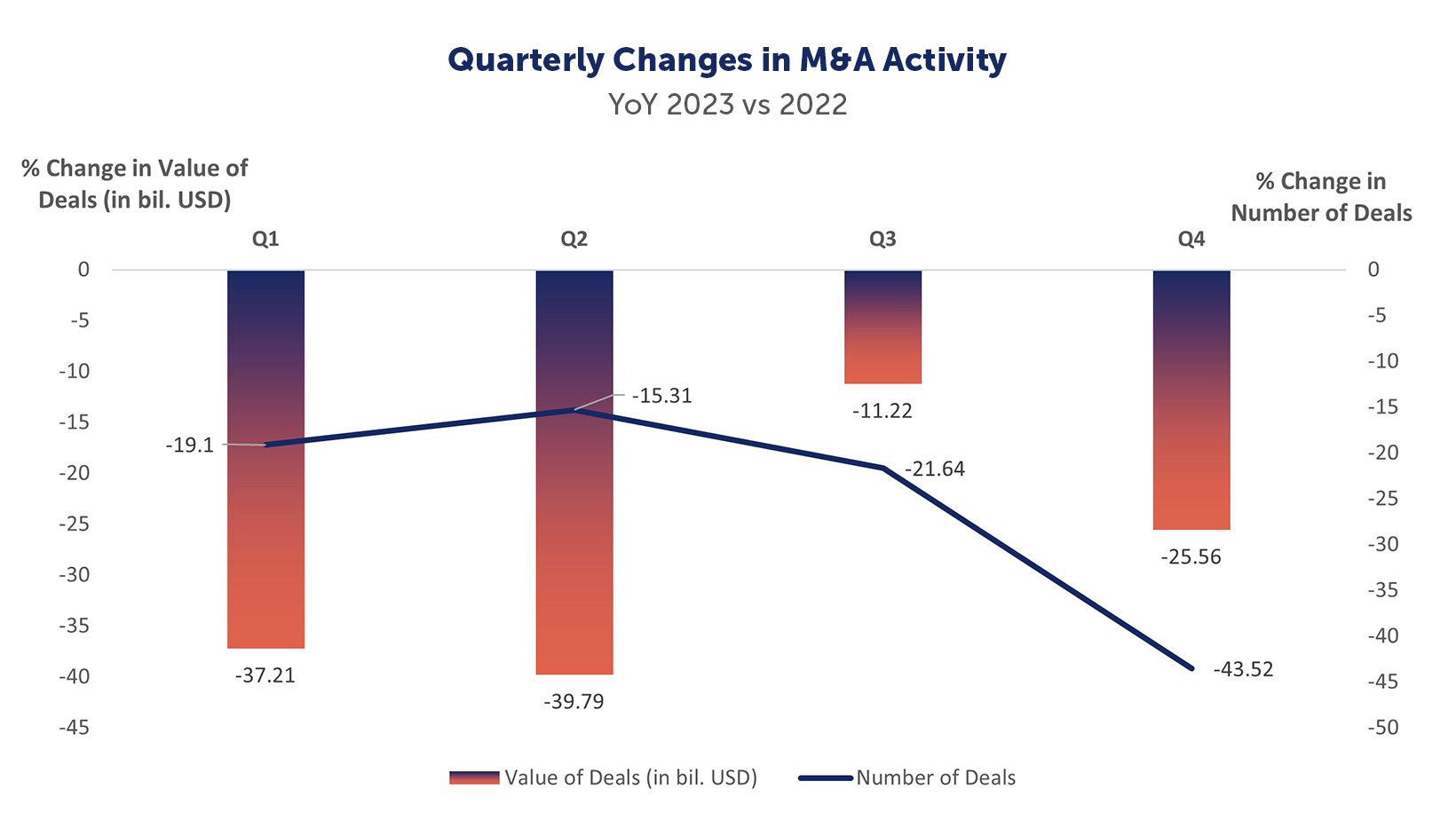
The quarterly analysis of 2023/2022 numbers find the largest decline of number of deals in the final quarter (Q4) at 43.5% and the largest decline of value of deals was in Q2 at 40%.
Table 3:
Quarterly Changes in M&A Activity, YoY 2023 vs 2022
2023 Percentage Change to 2022 | Number of Deals | Value of Deals (in bil. USD) |
Q1 | -19.10 | -37.21 |
Q2 | -15.31 | -39.79 |
Q3 | -21.64 | -11.22 |
Q4 | -43.52 | -25.56 |
Table 4:
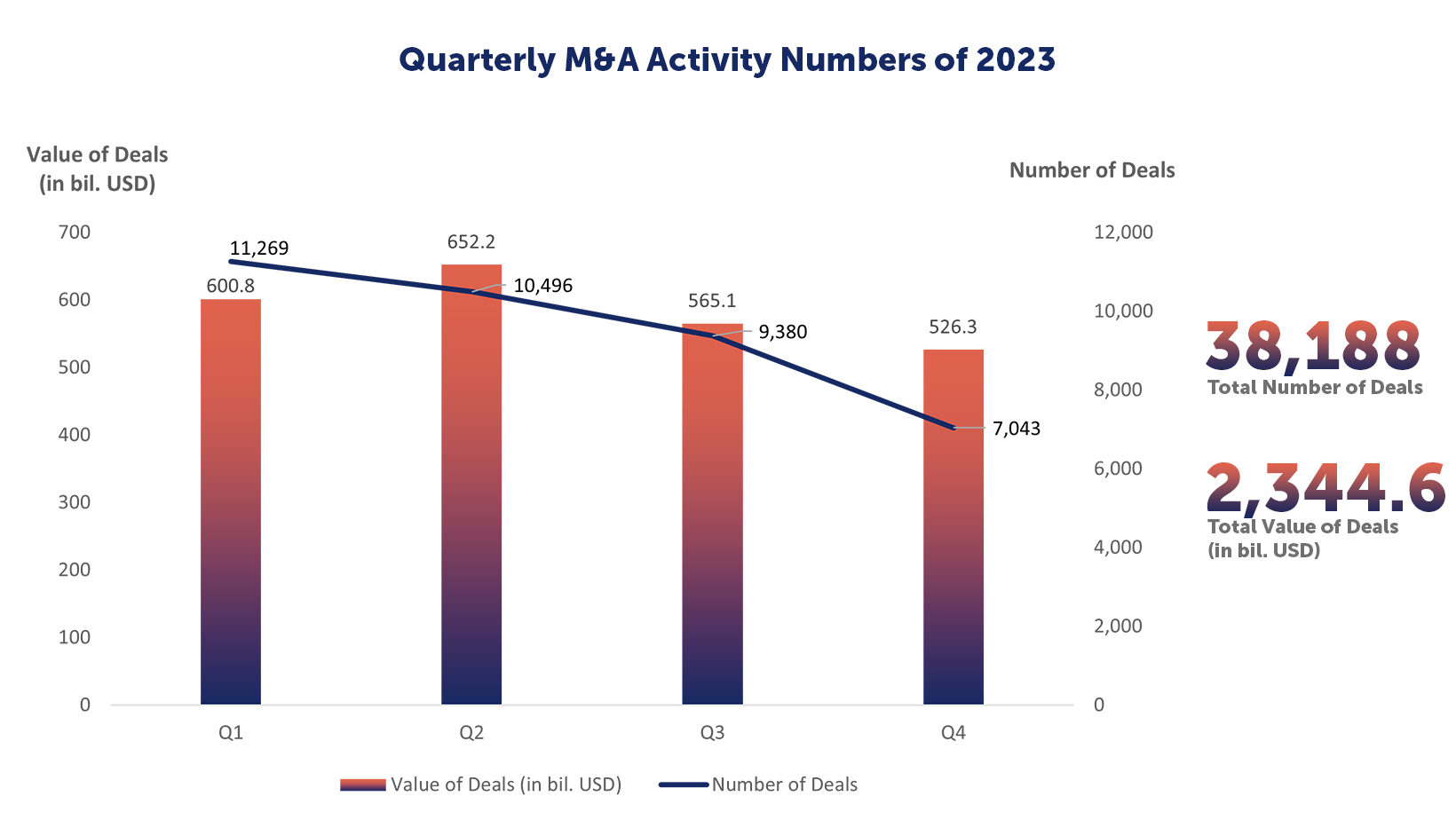
Quarterly M&A Activity Numbers of 2023
2023 | Number of Deals | Value of Deals (in bil. USD) |
Q1 | 11,269 | 600.8 |
Q2 | 10,496 | 652.2 |
Q3 | 9,380 | 565.1 |
Q4 | 7,043 | 526.3 |
Total | 38,188 | 2,344.6 |
Table 5:
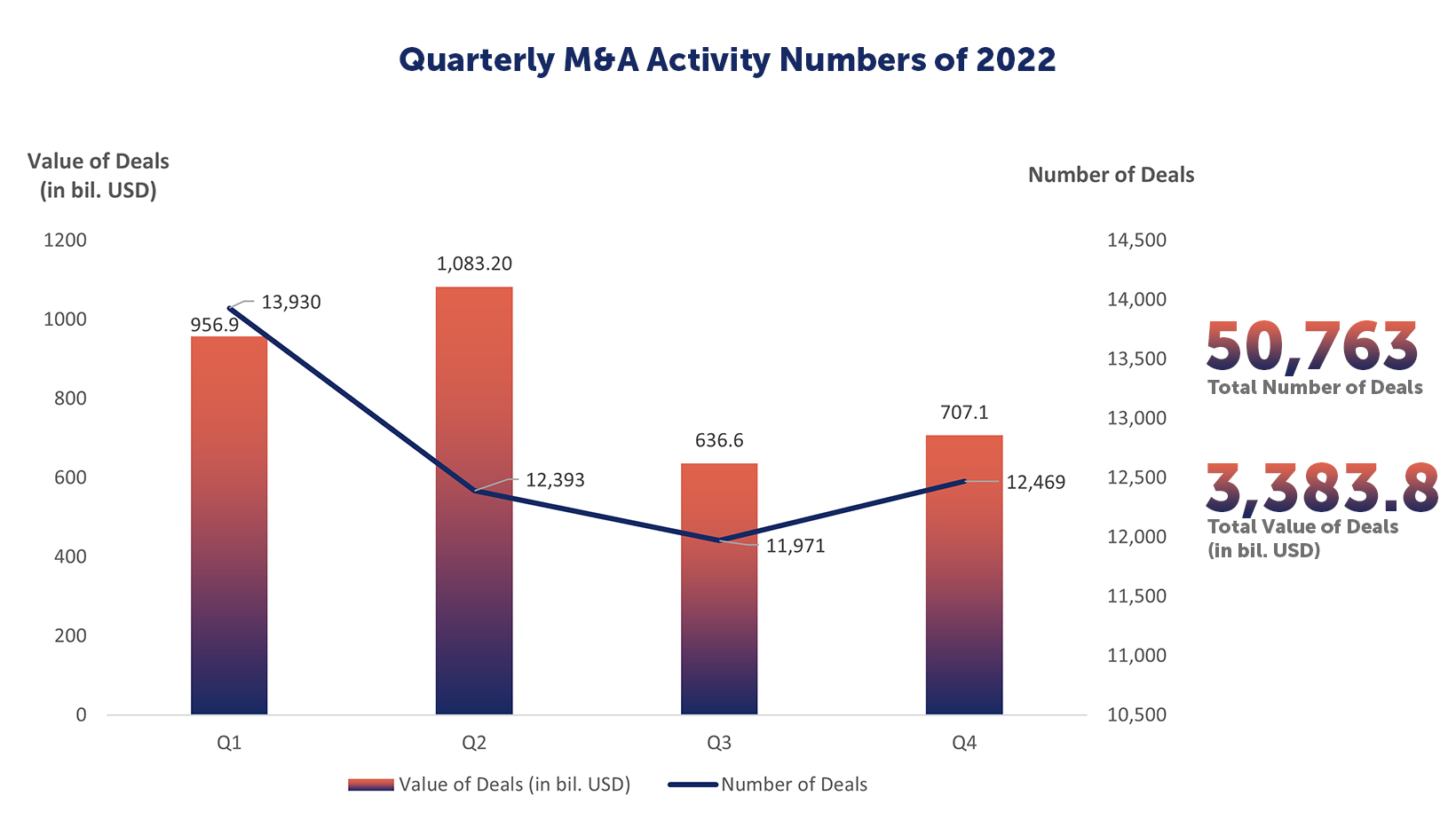
Quarterly M&A Activity Numbers of 2022
2022 | Number of Deals | Value of Deals (in bil. USD) |
Q1 | 13,930 | 956.9 |
Q2 | 12,393 | 1,083.2 |
Q3 | 11,971 | 636.6 |
Q4 | 12,469 | 707.1 |
Total | 50,763 | 3,383.8 |
What Happened in 2023?
In 2023, the global mergers and acquisitions landscape witnessed a noteworthy decline in comparison to the preceding year, due to substantially reduced deal volumes and values. This deceleration found its roots in a confluence of factors, encompassing the upswing in interest rates, the presence of inflationary pressures, and prevailing economic uncertainty coupled with geopolitical conflicts. Despite the overarching downturn, the year did not unfold devoid of significant occurrences.
Early 2023 M&A Activity Dynamics and Trends
Record-breaking levels of activity defined 2021, carrying forward their energy into the first part of 2022. Nevertheless, a slowdown emerged in the latter part of 2022, extending its impact into the early months of 2023, as noted in this 2023 mergers and acquisitions activity review.
Recalling the positive performance of 2021, the outset of 2022 showcased robust M&A activities, featuring numerous deals surpassing the USD 10 billion mark. However, during the latter part of the year, deal volumes experienced a decline influenced by various factors. Reduced corporate valuations diminished the motivation for buying or selling, while increasing interest rates made borrowing less attractive.
An M&A report published by PWC in January 2023, stated that “60% of global CEOs are not planning to delay M&A deals into 2023, even as deals activity falls below record 2021 levels on recession fears.” While this may have been the sentiment of the time, the data for 2023 does not support this in retrospect. In fact, 2023 may have been one the most turbulent years for M&A in the last decade. This happened even though the findings of the report suggested “Strategic M&A and portfolio optimization remain C-suite priority and key to business transformation in 2023.”
The midyear M&A report of Bain & Company stated that uncertainty in macroeconomics and interest rates persists, adding complexity to dealmaking and encouraging a sense of caution among both sellers and buyers. Job cuts have sped up, but the job market is holding strong. Inflation has eased off but is still present. While the expected recession hasn’t officially hit, executives are acting as if it has, emphasizing cost discipline and revisiting downturn strategies.
While there was a high number of interested buyers to do deals, there were “struggles to get the deals over the finish line.” The overarching fear of sellers was not to be selling at the market bottom, just as the market conditions would take a turn.
Mid-Year M&A Activity Challenges and Strategic Shifts
During the initial half of 2023, an inverted yield curve defined the period, indicating a situation where shorter-term debt instruments yield higher returns than their longer-term counterparts. This peculiar and unsustainable anomaly in bond market pricing reflects the market’s uncertainty regarding the timing and location of interest rate stabilization. This ongoing uncertainty added complexity to dealmaking and promoted a sense of caution among both sellers and buyers.
It was anticipated that there would be a rise in assets entering the market. This was based on the prediction that private equity exits will sooner than later happen due to portfolios maturing. At the same time the M&A community was preparing for helping divestments of businesses from corporate portfolios.
Private equity firms tend to hold onto investments for an average of three to five years. Considering the uptick in private equity investments in 2020 and 2021, that three-to-five-year time frame is here.
In September of 2023, Reuters quoted Tony Kim, Co-President of Centerview Partners: “… In 2023, the deals that are getting done are more like perfect fit deals. The buyer is the right buyer for the business, and they’re paying premium multiples for it. 2024 seems to be setting up to be more significant.”
Reuters further stated that the environment for financing leveraged buyouts remained difficult as central banks kept interest rates high. This situation led private equity firms to adopt alternative solutions like earn-out structures and contingent value rights (CVRs) to address disparities in pricing. For instance, Roark Capital’s acquisition of the sandwich chain Subway for USD 9.55 billion included the utilization of an earn-out structure.
Investment banking firms expressed optimism with healthy pipelines, the expectation was to surpass those of the past few years. Nevertheless, this positivity hasn’t translated into deals. Initial expectations for increased activity in Q3 shifted to Q4, and now some firms are considering 2023 a write-off, looking forward to 2024, stated in her mid-year review, Claudine Cohen of Cohn Reznick Advisory.
She further concluded that the M&A ecosystem is eager to resume operations, with high dry powder for transactions, but there’s a challenge in the availability of capital for new fundraising. While leveraging existing capital is beneficial in the short to medium term, investors need discipline, focusing on returns with a more enduring impact. The current M&A market is marked by uncertainty due to opposing forces, but, as with any business cycle, there will be ebbs and flows, and emergence from the current situation is expected.
Navigating Market Complexities and Anticipating Future Trends in M&A Deals
Later in October, an M&A report published by BCG confirmed that in 2023, mergers and acquisitions confronted its most enduring challenges since the 2008–2009 financial crisis. Factors like increasing interest rates, geopolitical uncertainties, and fears of a recession contributed to a decline in global deal activity. Yet, after reaching its lowest point in the first quarter of 2023, there are now observable indications of a revival in global M&A activity.
Jens Kengelbach, BCG’s global head of M&A and coauthor of the 20th edition of BCG’s Global M&A Report, expresses a relatively optimistic outlook for 2024. While there are promising signs of recovery in M&A deal activity, challenges persist for dealmakers. The higher cost of capital is a notable factor that will lead companies to carefully scrutinize large or transformative deals. In response, businesses may opt for acquisitions, divestitures, or a combination of both to enhance growth and reshape their operations.
Dealmakers are acknowledging the increasing complexity of global antitrust regulations, anticipating a reduction in the number of mega-deals. The focus is shifting towards deals valued between USD 1 billion to USD 10 billion in the foreseeable future. Navigating antitrust regulations has become challenging, with the U.S. now presenting similar difficulties as the European regulatory process, contributing to greater unpredictability. Some experts foresee the next two years as potential peaks for M&A exit activity in private equity, driven by the necessity for funds to return money to investors.
In the short term, a significant driver for dealmaking will be the plentiful available capital held by sovereign wealth funds, private equity and venture capital investors, along with some large companies.
Several factors that impact prices, including inflation levels, financing costs, and uncertainty, are showing signs of stabilization. As sellers progressively acknowledge this evolving norm in the coming months, it is anticipated that the gap between sellers’ and buyers’ expectations will diminish.
The Rise of AI in M&A
In 2023, a major trend in mergers and acquisitions revolves around digital transformation spurred by the adoption of AI. This trend is particularly pronounced in the financial sector, where companies grapple with the advantages and challenges associated with integrating AI for optimal growth.
Throughout the deal-making process, both acquiring and target entities are increasingly turning to AI tools for tasks such as mining, analyzing, and searching through due diligence data. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on evaluating the risks and rewards associated with the use of AI tools. Buyers, in particular, are urged to conduct a SWOT analysis-informed assessment of AI tools to gain a comprehensive understanding of how the target company’s business model will be bolstered by the incorporation of AI.
Resilience of Smaller M&A Deals and 2024 Outlook
The decline in M&A deal volumes seems to be particularly pronounced in larger deals, where those exceeding USD 1 billion experienced a drop more than twice that of deals valued under USD 1 billion.
Smaller M&A deals are demonstrating increased resilience and are expected to recover more quickly, primarily due to a couple of key factors. Firstly, their lesser susceptibility to volatility distinguishes them from larger deals, which are more influenced by global market forces. Consequently, smaller deals are less likely to be derailed by external factors.
Moreover, the cost-effectiveness of smaller deals contributes to their resilience. Companies have the option to finance these transactions through existing financial reserves or by liquidating assets, eliminating the necessity for external financing. This cost-efficient approach makes smaller deals less sensitive to high interest rates, unlike larger transactions that heavily depend on external financing.
According to EY, business leaders are anticipating a revival in the latest M&A trends as we progress into 2024. The most recent EY CEO Outlook Pulse survey reveals that 98% of CEOs expect to actively participate in strategic transactions within the next 12 months. This signifies a significant increase from the 89% reported in January 2023.
In Conclusion
In IMAA’s comprehensive mergers and acquisitions review, we have observed that in 2023, the M&A market witnessed a notable downturn, yet positive developments indicate the potential for a rebound in 2024. Amidst cautious optimism, several factors suggest a resurgence in deal activity:
Continued Capital Availability
Sovereign wealth funds, private equity firms, and venture capitalists retain substantial capital, providing a robust foundation for M&A activities, especially for strategic acquisitions aligning with long-term growth goals.
Rising AI Adoption
The increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping M&A transactions, enhancing efficiency and reducing costs throughout the process, from due diligence to integration.
Emphasis on Smaller Deals
Smaller deals exhibit greater resilience, attributed to lower valuations and the ability to be financed internally or through asset sales. As economic conditions improve, smaller deals are anticipated to play a more significant role in the M&A landscape.
To capitalize on these opportunities, companies are advised to adapt to the evolving M&A environment:
Strategic Rationale for Acquisitions
Companies should carefully evaluate the strategic fit and long-term value of potential acquisitions, focusing on those aligned with core business objectives to drive sustainable growth.
AI Integration for Efficiency and Risk Management
Leveraging AI tools for streamlined due diligence, risk identification, and optimized deal structures will enhance operational efficiency and risk management.
Focus on Smaller, Focused Deals
Pursuing smaller deals, less susceptible to market fluctuations, allows financing with internal resources or asset sales. This approach may unveil opportunities for acquiring undervalued assets or forming strategic partnerships.
Steering the M&A landscape in 2024 requires strategic thinking, operational efficiency, and effective risk management. Companies adaptable to the evolving environment, seizing emerging opportunities, are well-positioned for success. While challenges persist, signs of recovery offer potential for those pursuing strategic, value-enhancing acquisitions to thrive in 2024 and beyond.
For ongoing in-depth insights into mergers and acquisitions, be sure to check out our weekly global M&A deal updates and monthly industry-specific M&A activity reports


Stay up to date with M&A news!
Subscribe to our newsletter